There’s little in retailing that Walmart Inc. and Target Corp. aren’t prepared to handle. So it was jarring that over a 24-hour period the two scions of the trade posted weak first-quarter profits that appeared to blindside their management teams.
Part of the bottom-line blowup was due to fuel, which soared to record highs following Russia’s Feb. 24 invasion of Ukraine. Part of it was due to margin pressures caused by an unfavorable sales mix as consumers shifted their buying from higher-margin goods like electronics to less profitable items like groceries. An extension of that was an overshoot of inventory-stocking activity, which came back to bite the retailers after waning concerns over the COVID-19 pandemic pushed more consumer buying toward services and “experiences” and away from goods.
There’s little that retailers can do about fuel prices. It can be argued they should have expected the pandemic-driven buying spree from March 2020 until the end of 2021 to peter out and that they should have planned their inventory strategies accordingly. Yet demand forecasting has always been a tough nut to crack, and the market is where it is. Inventory build may also have been the result of supply chain delays at the start of the year that resulted in some late deliveries of impaired freight.
Inventory levels as of March, when compared to activity in March 2019 after inventories stabilized following a major pull-forward in 2018 ahead of the Trump administration’s China tariffs, produce a mixed bag of results. Unsurprisingly given the current dearth of motor vehicles, the ratio of vehicle and parts inventories to sales has fallen considerably, according to federal government data analyzed by Michigan State University. Apparel inventories to sales also declined over those periods, as did e-commerce.
However, furniture, home furnishings and appliances, building materials and garden equipment, and a category known as “other general merchandise,” which includes Walmart and Target, among others, reported higher inventory-to-sales ratios, according to government data analyzed by Michigan State.
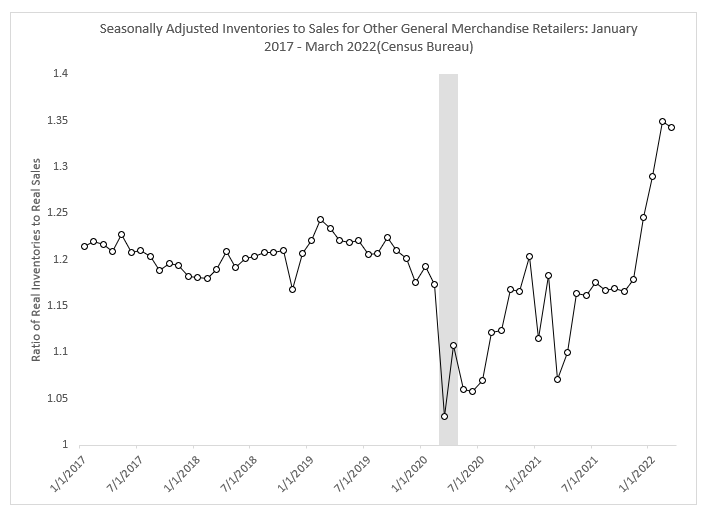
For the latter sectors, the change has happened fast, according to Jason Miller, logistics professor at MSU’s Eli Broad College of Business. As of November, inventory-to-sales ratios were at pre-COVID levels, Miller said. They have since exploded upward.
Miller said he expects a “cooldown” in retailer order volumes, even if inflation-adjusted sales stay constant, as retailers look to reduce their existing stock. He also expects retailers to launch major discounting programs to expedite the inventory burn. Fewer orders within certain categories bodes ill for carriers whose networks are strongly tied to inbound lanes to retailers’ distribution centers, Miller said.
In a Friday note, Bascome Majors, analyst for Susquehanna Investment Group, said that the spread between year-over-year sales and inventories — a rough barometer of the impact of higher sales on restocking activity — turned positive in spring 2020 and accelerated in favorable territory for four consecutive quarters. Gradually, however, the spread has turned negative, according to Majors. In this year’s first quarter, inventory growth exceeded sales growth by 200 basis points. The recent surge in inflation, Majors wrote, has severely distorted inventory and sales trends.
Freight recession priced in?
For some, high inventory levels are an expected occurrence and should be welcomed. In a Tuesday note, Amit Mehrotra, transport analyst at Deutsche Bank, said rising buffer stock is part of retailers’ desire to have goods available when consumers scan the shelves. Mehrotra added, however, that the data points translate into a likely slowdown in freight flows in the coming months and quarters.
He said that a recession is already priced into most transportation equities, noting that the shares of most trucking companies are higher over the past 30 days while the broader market is about 7% lower.
In an unusual world, Walmart, Target and other retailers are likely to turn to the one area where they’ve traditionally found leverage: their shipping bill. During the quarter, Target (NYSE: TGT) faced freight and transportation costs that were hundreds of millions of dollars above already-elevated expectations, COO John Mulligan said on the company’s Wednesday analyst call. It was essentially the same story at Walmart (NYSE: WMT).
Retailers’ efforts to rein in transportation costs will translate into an unprecedented third and even fourth round of truckload contract negotiations, with users getting more aggressive in their bids to extract greater cost savings, according to industry experts.
The discussions could get contentious. In a LinkedIn post on Friday, Jason Ickert, president of trucking firm Sonwil Logistics, said a large shipper that Ickert wouldn’t identify suggested on a conference call this week with truckload carriers that they were “artificially propping up their rates” above accepted market levels. The shipper “stated clearly” that the carriers were expected to adjust their rates during what would be an “unprecedented and unplanned” third round of request for proposals, Ickert wrote.
A potential shift to intermodal
Pressures to drive down transport expenses will also trigger increased interest in intermodal, whose all-in costs are cheaper relative to contract truckload than at any time since 2018. Intermodal rates have risen at a slower pace than truckload contract rates, a turnabout from the 2019 freight recession when higher intermodal rates allowed over-the-road transport to gain market share.
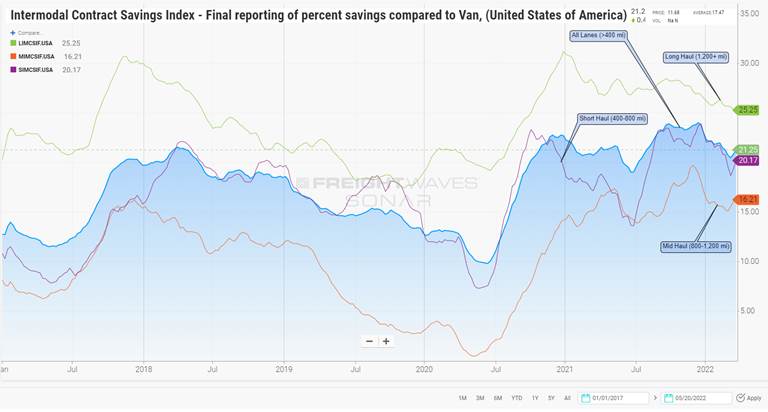
The shift to intermodal, if it happens, would benefit the railroads and intermodal marketers like J.B. Hunt Transport Services Inc. (NASDAQ: JBHT), Hub Group Inc. (NASDAQ: HUBG) and Schneider Inc. (NASDAQ: SNDR). However, experts caution that intermodal capacity remains constrained, as does warehouse space needed to store the stuff.
“Walmart, Target and other retailers will soak up every drop of intermodal capacity that Hunt, Hub, Schneider and the rails deliver in 2022 and probably in 2023,” said Majors of Susquehanna Investment Group. The elevated level of activity, he said, should occur even if retailers are working through a multiquarter process of de-stocking.







